
Cloud Security Services: A Technical Guide to Securing Modern Cloud Environments

Cloud computing has fundamentally transformed how infrastructure, applications, and data are deployed and scaled. While platforms such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud provide strong native security controls, cloud security is governed by a shared responsibility model, where customers are responsible for securing their own workloads, identities, configurations, and data.
Cloud Security Services help organizations implement continuous, scalable, and identity-driven security across modern cloud environments, enabling them to maintain innovation without interruption.
What Are Cloud Security Services?
Cloud security services are integrated security solutions and managed operations designed to protect cloud infrastructure, workloads, applications, APIs, and data across:
-
Public cloud environments (AWS, Azure, GCP)
-
Hybrid cloud architectures
-
Multi-cloud deployments
-
Containerized and serverless workloads.
These services combine cloud-native security tools, automation, policy enforcement, and expert oversight to reduce risk and maintain a strong security posture at scale.
Cloud Security in the Shared Responsibility Model
In cloud environments, security responsibilities are divided between the cloud provider and the customer.
Cloud Provider Responsibilities
-
Physical data center security
-
Underlying hardware and network infrastructure
-
Virtualization layer and cloud fabric security
Customer Responsibilities
-
Identity and access management (IAM)
-
Network configuration and access controls
-
Operating system and application security
-
Data protection and encryption
-
Monitoring, logging, and compliance
Most cloud breaches occur within customer-controlled layers, making cloud security services essential.
Core Technical Domains of Cloud Security Services
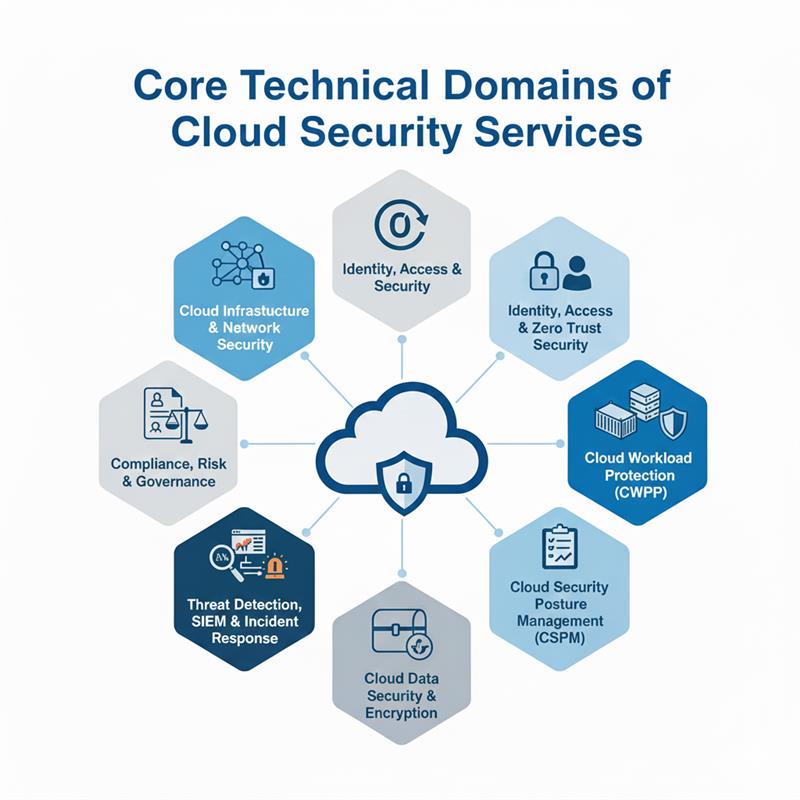
Cloud Infrastructure & Network Security
Secures the foundational cloud architecture and network boundaries.
Key capabilities:
-
Secure VPC / VNet architecture and segmentation
-
Network security groups and access control lists
-
Cloud firewalls and Web Application Firewalls (WAF)
-
DDoS mitigation and traffic filtering
-
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Security objective: Reduce attack surface and prevent lateral movement.
Identity, Access & Zero Trust Security
In cloud environments, identity becomes the primary security perimeter.
Technical focus areas:
-
Least-privilege IAM policies
-
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
-
Privileged Access Management (PAM)
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
-
Identity federation (SAML, OAuth, OIDC)
-
Continuous identity posture monitoring
Security objective: Prevent credential compromise and unauthorized access.
Cloud Workload Protection (CWPP)
Protects workloads running across virtual machines, containers, and Kubernetes.
Includes:
-
Host-based intrusion detection
-
Container and Kubernetes runtime security
-
Image and workload vulnerability scanning
-
File integrity monitoring
-
Behavioral threat detection
Security objective: Detect and block malicious activity at runtime.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Continuously identifies and remediates cloud misconfigurations.
Technical capabilities:
-
Continuous configuration assessment
-
Policy-as-code enforcement
-
Benchmark mapping (CIS, NIST, ISO, SOC)
-
Automated remediation workflows
-
Drift detection in Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC)
Security objective: Eliminate misconfigurations, the leading cause of cloud breaches.
Cloud Data Security & Encryption
Protects sensitive data stored and processed in cloud environments.
Includes:
-
Encryption at rest and in transit
-
Cloud Key Management Systems (KMS)
-
Customer-managed encryption keys
-
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
-
Backup and disaster recovery strategies
Security objective: Maintain confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
Threat Detection, SIEM & Incident Response
Provides centralized visibility and real-time threat detection.
Key components:
-
Cloud audit logs and telemetry
-
SIEM correlation and alerting
-
Threat intelligence integration
-
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
-
SOAR-driven automated response
Security objective: Reduce Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR).
Compliance, Risk & Governance
Aligns cloud security controls with regulatory and industry standards.
Supported frameworks include:
-
ISO 27001
-
SOC 2
-
HIPAA
-
PCI-DSS
-
GDPR
-
NIST CSF
Capabilities:
-
Continuous compliance monitoring
-
Audit evidence collection
-
Risk assessment and reporting
-
Cloud governance enforcement
Managed Cloud Security Services (MCSS)
Managed Cloud Security Services provide 24/7 operational security ownership, including:
-
Continuous monitoring and alert triage
-
Incident investigation and response
-
Cloud security configuration management
-
Compliance reporting and posture tracking
-
Ongoing hardening and optimization
This model is ideal for organizations that:
-
Lack of in-house cloud security expertise.
-
Operate hybrid or multi-cloud environments.
-
Require continuous SOC coverage.
Common Cloud Security Threats Addressed
-
Cloud misconfigurations
-
Insecure APIs and integrations
-
Credential theft and privilege abuse
-
Ransomware targeting cloud workloads
-
Supply-chain and SaaS risks
-
Insider threats
Cloud security services apply defense-in-depth and continuous monitoring to mitigate these risks.
Benefits of Technical Cloud Security Services
-
Centralized security visibility
-
Reduced human and configuration errors
-
Faster detection and response to threats
-
Secure DevSecOps and CI/CD pipelines
-
Continuous compliance readiness
-
Improved cloud resilience and uptime
How to Select a Cloud Security Services Provider
When evaluating a provider, consider:
How AS13.ai Approaches Cloud Security Services
AS13.ai delivers cloud-native, security-first cloud services designed for modern enterprises operating across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
AS13.ai’s cloud security approach focuses on:
-
Secure cloud architecture and design
-
Identity-centric Zero Trust security
-
Cloud workload and posture protection
-
Continuous threat detection and monitoring
-
Compliance-driven cloud governance
By aligning security with cloud operations, AS13.ai helps organizations scale securely without compromising performance, compliance, or agility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Cloud security services protect cloud infrastructure, workloads, applications, identities, and data using continuous monitoring, threat detection, policy enforcement, and compliance controls.
Cloud security is identity-driven, automated, API-based, and continuously monitored, unlike traditional perimeter-based security models.
CSPM focuses on cloud configuration and compliance, while CWPP protects workloads such as VMs, containers, and Kubernetes at runtime.
No. Cloud providers secure the underlying infrastructure, while customers are responsible for IAM, configurations, data protection, and workload security.
Managed services are ideal when organizations lack internal expertise, require 24/7 monitoring, or operate complex multi-cloud environments.
From secure cloud architecture to 24/7 monitoring and compliance-driven security operations.















